Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Tips About What Is ELCB Vs MCB

Pin On Kc
ELCB vs. MCB
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever stared at your electrical panel and wondered what all those little switches actually do? You're not alone! It can feel like deciphering an alien language. Two of the most common components you'll find are ELCBs (Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers) and MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers). Both are safety devices, but they protect against different electrical problems. Think of them as electrical superheroes, each with their own special power. One prevents shocks, the other prevents fires (mostly!).
The core difference lies in what triggers them to trip. An MCB is like a bodyguard for your wiring, stepping in when there's too much current flowing through a circuit. This "overcurrent" situation could be caused by an overload (too many appliances plugged in) or a short circuit (a direct connection between live and neutral wires, which is VERY bad). An ELCB, on the other hand, is much more sensitive and looks for leakage current. It detects if electricity is escaping from its intended path, usually through a person touching a live wire or faulty appliance.
Imagine your washing machine has a tiny crack in its wiring, and electricity is leaking to the metal casing. If someone touches the machine while standing on a damp floor, they could get a nasty shock. An ELCB will detect this leakage and trip, cutting off the power before serious harm occurs. An MCB might not trip in this scenario because the leakage current might not be high enough to trigger its overcurrent protection.
In essence, MCBs are designed to prevent damage to your electrical system from overloads and short circuits, while ELCBs are primarily focused on protecting people from electric shock. Knowing the difference is crucial for home safety, and this article will help you understand these devices like a pro.

MCB
2. How Miniature Circuit Breakers Work
MCBs are the workhorses of your electrical panel, diligently monitoring the current flowing through each circuit. They operate on two primary mechanisms: thermal and magnetic. The thermal mechanism involves a bimetallic strip that heats up and bends when the current exceeds the rated value. This bending action triggers the tripping mechanism, cutting off the power. The magnetic mechanism uses an electromagnet that trips the breaker almost instantly when a very high current, like that from a short circuit, flows through it.
Think of it like this: you're driving on the highway (the electrical circuit). The speed limit (the current rating of the MCB) is 65 mph. If you start speeding (overload), the thermal mechanism slowly kicks in, like a friendly warning before you get a ticket. If you suddenly crash into a wall (short circuit), the magnetic mechanism acts immediately, like an airbag deploying to protect you. The time it takes for an MCB to trip depends on how much the current exceeds its rated value. A small overload might take a few seconds to trip, while a short circuit will trip almost instantaneously.
MCBs are typically rated in amps (A), indicating the maximum current they can safely handle. Common ratings include 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, and 32A. It's important to choose the correct MCB rating for each circuit to ensure proper protection. Using an MCB with too low a rating will cause nuisance tripping (the breaker keeps tripping even under normal load), while using one with too high a rating could allow an overload to continue, potentially damaging wiring or causing a fire.
So, the next time you see an MCB, remember it's not just a switch; it's a sophisticated device designed to protect your home and your appliances from the dangers of overcurrents and short circuits. Making sure you have the right MCBs is super important. It's like making sure you have the right tires on your car; you don't want to risk a flat tire... or worse, an electrical fire! And if you're not sure what you're doing, call a professional electrician. They're like the mechanics of the electrical world, and they'll make sure everything is running smoothly.
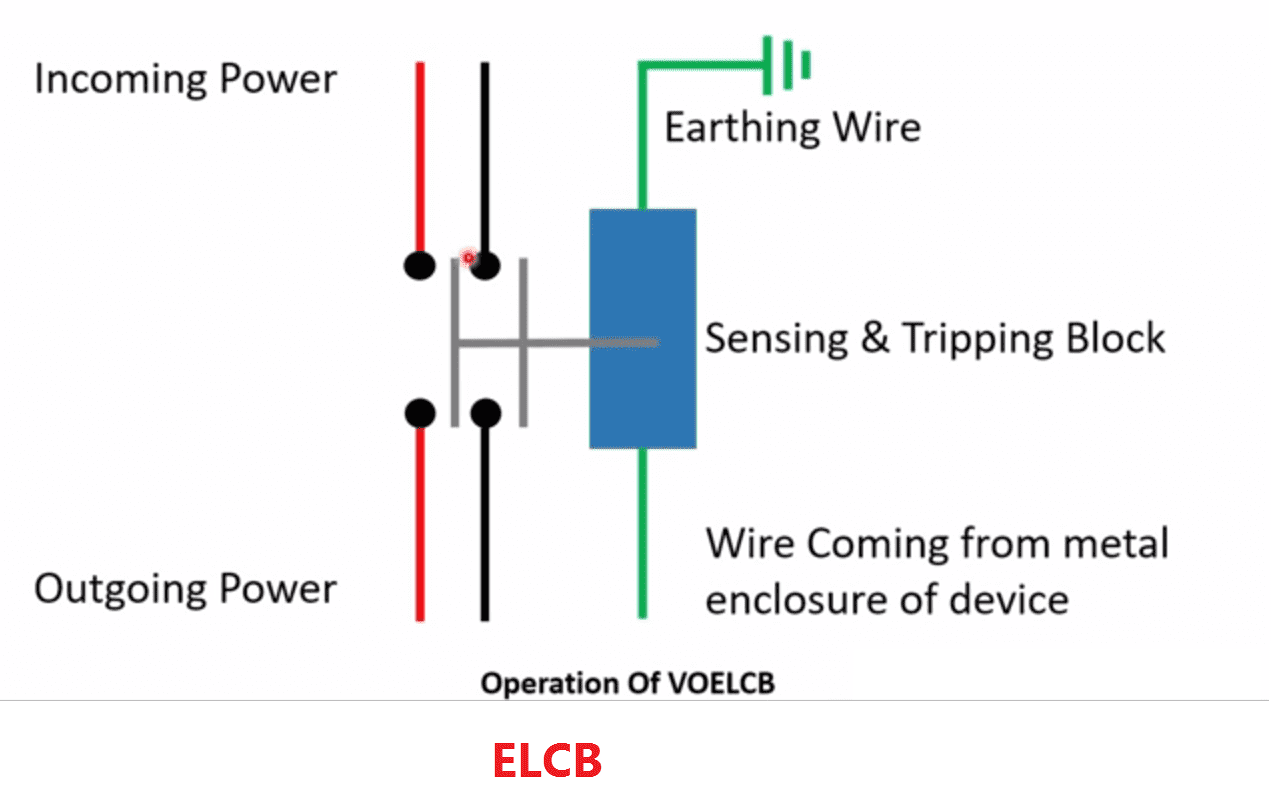
ELCB
3. Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers Explained
ELCBs are designed to protect against a very specific hazard: electric shock. They do this by constantly monitoring the balance of current flowing through the live (hot) and neutral wires in a circuit. Under normal circumstances, the current flowing into an appliance through the live wire should be exactly the same as the current flowing back out through the neutral wire. An ELCB detects even a tiny difference between these currents, indicating that some electricity is leaking to earth (ground).
This "leakage current" is often the result of a fault in an appliance, damaged wiring, or someone accidentally touching a live wire. When the ELCB detects a leakage current exceeding its sensitivity threshold (typically 30mA), it trips almost instantly, cutting off the power and preventing a potentially fatal electric shock. Think of it as a super-sensitive electrical lifeguard, always on the lookout for danger and ready to jump in to save the day.
ELCBs are particularly important in areas where there's a high risk of electric shock, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas. They provide an extra layer of protection beyond what MCBs offer. While an MCB protects against overloads and short circuits that can damage your wiring, an ELCB protects people from electrocution. It's important to note that ELCBs are becoming less common in newer installations, often replaced by RCDs (Residual Current Devices), which offer similar protection but are more versatile and less prone to nuisance tripping.
Imagine you're using a power drill outside, and the cable gets damaged, exposing the live wire. If you accidentally touch the exposed wire while standing on damp ground, the electricity will flow through your body to earth, causing an electric shock. An ELCB will detect this leakage current and trip almost instantly, preventing serious injury or death. That's why ELCBs are so important, they're like the unsung heroes of electrical safety, quietly protecting us from unseen dangers. So, give your ELCB a silent thank you next time you're doing some DIY, it might just save your life!

ELCB vs. MCB
4. Choosing the Right Protection
Let's break down the key differences between ELCB vs MCB, to make it crystal clear. An MCB protects the wiring from overcurrents and short circuits, preventing damage to your electrical system and reducing the risk of fire. An ELCB protects people from electric shock by detecting leakage currents. MCBs are rated in amps (A), while ELCBs are rated in milliamps (mA) and specify the tripping current. An MCB trips when the current exceeds its rated value for a sustained period, while an ELCB trips when it detects a leakage current above its sensitivity threshold.
While MCBs are essential in every electrical circuit, ELCBs are particularly crucial in areas with a high risk of electric shock. They provide a vital layer of protection, especially in older installations where earthing systems might not be as effective. However, modern electrical installations often use RCDs (Residual Current Devices) instead of ELCBs. RCDs offer similar protection to ELCBs but are more versatile and less susceptible to nuisance tripping. They are also more sensitive to detecting leakage current, providing even greater protection against electric shock.
Think of it this way: MCBs are like the seatbelts in your car, protecting you in a crash (overload or short circuit). ELCBs are like the airbags, providing an extra layer of protection in a more specific type of accident (electric shock). While seatbelts are essential, airbags can be life-saving in certain situations. Similarly, MCBs are a fundamental part of electrical safety, but ELCBs (or RCDs) offer an additional level of protection that can be crucial in preventing serious injury.
Ultimately, choosing the right protection depends on your specific needs and the electrical system in your home. Consulting a qualified electrician is always recommended to ensure that your electrical system is safe and properly protected. They can assess your needs, recommend the appropriate devices, and ensure that everything is installed correctly. After all, electricity is a powerful force, and it's always better to be safe than sorry!

What Is Mcb Rcbo Rccb Mccb Elcb? Difference Between Mcb,, 53 OFF
RCDs
5. Why Residual Current Devices Are Gaining Popularity
While this article focuses on ELCB vs MCB, it's important to acknowledge that RCDs (Residual Current Devices) are increasingly becoming the go-to choice for earth leakage protection in modern electrical installations. RCDs offer several advantages over traditional ELCBs, making them a more versatile and reliable option. One of the key advantages is their ability to detect leakage current regardless of the earthing system, whereas ELCBs rely on a properly functioning earth wire to operate effectively.
Another significant advantage of RCDs is their reduced susceptibility to nuisance tripping. ELCBs can sometimes trip due to minor earth leakage currents caused by electronic devices, leading to unnecessary power outages. RCDs are designed to be more tolerant of these minor leakage currents, minimizing the risk of nuisance tripping. They also offer better sensitivity and faster response times, providing even greater protection against electric shock. This means they can detect and respond to leakage currents more quickly than ELCBs, potentially preventing more serious injuries.
RCDs come in various types, including RCBOs (Residual Current Breakers with Overload protection), which combine the functions of an RCD and an MCB in a single device. This simplifies installation and reduces the number of devices required in the electrical panel. RCBOs are becoming increasingly popular in new homes and renovations, offering comprehensive protection against both overcurrents and earth leakage. Essentially, you get the benefit of both an ELCB and an MCB in one neat package!
So, while understanding the differences between ELCBs and MCBs is essential for understanding basic electrical safety, it's also important to be aware of the advancements in technology that are making our homes safer. RCDs are a prime example of this, offering a more reliable and versatile solution for earth leakage protection. If you're upgrading your electrical system, be sure to consider RCDs as a modern and effective way to protect your family from the dangers of electric shock. It's like upgrading from a flip phone to a smartphone — you get more features, better performance, and enhanced safety!

Difference Between MCB, MCCB, MPCB, RCCB & ELCB And Its Working
FAQ
6. Addressing Common Concerns
Alright, let's tackle some of those nagging questions you might still have. Electricity can be confusing, so don't worry if you're not an expert!
Q: Can an ELCB replace an MCB?A: Nope! They serve different purposes. You need both. Think of it like needing both brakes and a steering wheel in your car — one doesn't replace the other, they work together for safety.
Q: How do I test if my ELCB is working correctly?A: Most ELCBs have a test button. Press it! If the ELCB trips, it's working. If it doesn't, you need to call an electrician. This test simulates a leakage current and confirms that the ELCB is able to disconnect the power.
Q: My breaker keeps tripping. What should I do?A: First, try resetting it. If it trips again immediately, there's a problem. Unplug any appliances on that circuit and try again. If it still trips, call an electrician. A constantly tripping breaker could indicate an overload, a short circuit, or a faulty appliance. Don't ignore it!