Heartwarming Tips About What Color Wire For 240V 3-phase

Understanding 208v 3 Phase Wiring A Comprehensive Diagram Guide
Decoding the Rainbow
1. Understanding the Importance of Color Codes
Ever stared into an electrical panel and felt like you were staring at a plate of spaghetti gone wrong? All those wires, seemingly a chaotic mess, each has a purpose, and more importantly, a designated color. These aren't just random hues someone picked out for fun; they're crucial for safety, troubleshooting, and ensuring your 240V 3-phase system purrs like a kitten (a very powerful, electrically-driven kitten, that is). Getting it wrong can lead to some seriously shocking consequences, literally!
Think of wire color codes like traffic lights. Red means stop (well, usually danger in electrical contexts), green means go (or ground), and yellow well, yellow often gets overlooked but its still important! It's all about quickly identifying the function of each wire without having to trace it back to its source. This saves time, reduces the risk of errors, and can even prevent life-threatening accidents. Imagine trying to defuse a bomb without knowing which wire to cut yeah, thats kind of what working on an improperly wired electrical system feels like.
Now, before we dive into the specifics of 240V 3-phase systems, it's worth noting that color codes can vary slightly depending on your location and the specific electrical code in place. So, always, and I mean always, consult your local regulations and a qualified electrician to make sure you're playing by the rules. Think of it as knowing the local laws before you decide to build a treehouse you don't want to get fined, or worse, electrocuted!
Ultimately, understanding these color codes is about respect for electricity and safety. Its about acknowledging the power you're dealing with and taking the necessary precautions to avoid becoming part of a Darwin Award nomination. So, let's get those colors straight and make sure your electrical work is both functional and safe.
The 240V 3-Phase Color Palette
2. Breaking Down the Standard Colors
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks (or copper wires, in this case). For a 240V 3-phase system, you'll typically encounter the following color scheme, based on the US standard, but as always, double-check local codes before putting on your gloves! Remember, safety first, then coffee (or whatever your preferred beverage is after a job well done).
Generally speaking, in the US system: You'll find Black, Red, and Blue used for the three hot wires (the ones carrying the juice!). These are your phases, labeled A, B, and C, respectively. Then, you'll generally see White being used for the neutral wire. Finally, there is Green (or bare copper) designated for the ground wire. Remember, these are the typical colors in the U.S. and things can change depending on the location or local laws.
A word of caution about older installations: you might find some funky stuff. Old wiring might not adhere to modern color codes, so treat any electrical work in older buildings with extra care. Always test and verify before you start messing around. And if you're not sure, call a professional. Trust me, it's cheaper than a trip to the emergency room or calling an electrician after you've already caused a sparky problem.
Using the proper colors isn't just about aesthetics; its about clarity and future-proofing your work. It ensures that anyone who works on the system after you will immediately understand the function of each wire. Its a professional courtesy, a safety measure, and just plain good practice. So, stick to the colors, and you'll be doing yourself and everyone else a favor. We wouldn't want things to get... shocking!

Why Color Codes Matter
3. Illustrating the Importance Through a Scenario
Okay, let's imagine a scenario: You're called in to troubleshoot a malfunctioning motor in a small workshop. The previous "electrician" (and I use that term loosely) didn't bother with color codes. Every wire is the same shade of gray, like a monotone nightmare. Where do you even begin?—You'd have to laboriously trace each wire back to its source, testing and verifying as you go. This eats up time, increases the risk of errors, and makes the whole process a massive headache.
Now, picture the same scenario, but this time, the wiring is properly color-coded. You immediately see the black, red, and blue wires feeding the motor, the white neutral, and the green ground. You can quickly identify the potential problem areas and focus your troubleshooting efforts. Youve just saved yourself hours of work and a whole lot of frustration. Plus, youre less likely to accidentally short something out and cause a small explosion. (Okay, maybe not an explosion, but definitely some sparks and a bad smell.)
The difference is like navigating a city with a clear map versus trying to find your way using only vague descriptions. Color codes are the map for your electrical system, guiding you to the right place quickly and safely. Without them, you're essentially wandering in the dark, hoping you don't stumble over something dangerous. And in the world of electricity, "dangerous" can mean anything from a minor shock to a major fire.
It goes beyond just troubleshooting too. If the proper colors are in place, it is easier for anyone to replace equipment or add new components. So using proper wiring colors is an investment in ease of maintainence, and ease of future upgrades. That is never a bad thing in the long run.
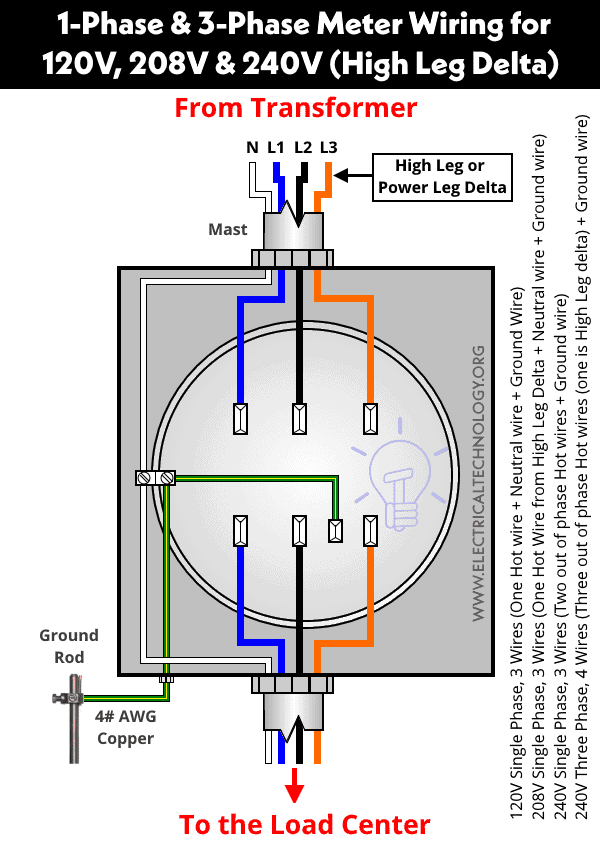
240v 3 Phase 4 Wire
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
4. Tips for Staying on the Straight and Narrow
Even with the best intentions, it's easy to make mistakes when wiring a 240V 3-phase system. Here are a few common pitfalls and how to steer clear of them:
First: Ignoring Local Codes. This is a big one. As mentioned before, color codes can vary by location. Don't assume that what worked in one place will work in another. Always check your local electrical codes before you start any work. Its the equivalent of checking the weather forecast before you head out you might need an umbrella (or a voltage tester, in this case).
Second: Assuming Everything is Correct. Just because the previous installer used a certain color scheme doesn't mean it's right. Always verify the wiring with a multimeter before you start working on anything. Trust, but verify, as they say. Or, in this case, distrust and verify.
Third: Using Tape to Re-Color Wires. While it might seem like a quick fix, using electrical tape to change the color of a wire is generally frowned upon (and may even be against code in some areas). It's not a permanent solution, and the tape can come loose over time, leading to confusion and potential hazards. Bite the bullet and use the correct color wires from the start. Your future self will thank you for it. Just like your future self will thank you for not eating that questionable gas station sushi.
Fourth: Neglecting to Label. Even if your wiring is perfectly color-coded, it's still a good idea to label each wire at both ends. This provides an extra layer of clarity and makes troubleshooting even easier. Think of it as adding subtitles to a movie it just makes everything clearer.
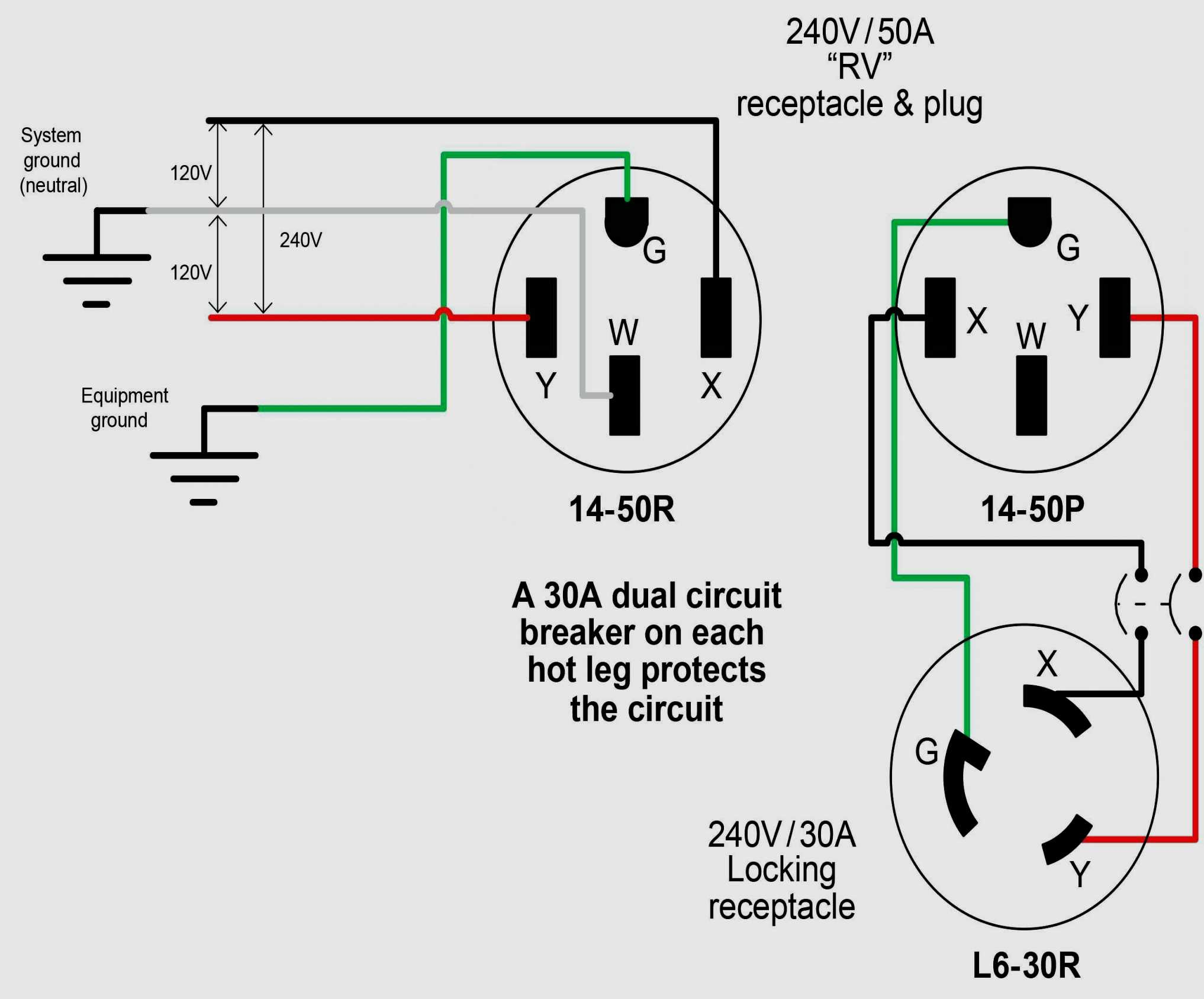
3 Phase 240v Wiring
FAQ
5. Clearing Up Common Confusions
Still scratching your head about wire colors? Here are some frequently asked questions to help clear things up:
Q: What happens if I use the wrong color wire?A: Using the wrong color wire can lead to confusion, troubleshooting headaches, and potentially dangerous situations. It can make it difficult for others to work on the system in the future, and it increases the risk of accidental shorts or misconnections. Ultimately, it's just not worth the risk.
Q: Can I use different colors if I label the wires clearly?A: While labeling is helpful, it's generally best to stick to the standard color codes whenever possible. Using different colors, even with labels, can still create confusion and increase the risk of errors. Think of it as speaking a different language even if you provide a translation, it's still easier to use the common language from the start.
Q: What if I'm working with an older system that doesn't follow modern color codes?A: If you're working with an older system, proceed with extreme caution. Carefully trace and identify each wire before you start any work. Use a multimeter to verify the voltage and polarity of each wire. And if you're not sure, call a qualified electrician. It's better to be safe than sorry.
Q: Where can I find the specific color code requirements for my area?A: Check your local electrical codes and regulations. You can usually find this information online or by contacting your local building department. You can also consult with a qualified electrician in your area.
