Marvelous Info About Is LAN-1 Faster Than LAN-2

What Is Lan Local Area Network Definition Of Vrogue
Unraveling the LAN Speed Mystery
1. What's the Deal with LAN Speeds Anyway?
Okay, so you're probably staring at your network settings, scratching your head, and wondering, "Is LAN-1 faster than LAN-2?" It's a valid question! We've all been there, staring at a screen willing our internet to cooperate. The truth is, determining which LAN connection is faster isnt always a straightforward comparison. It really depends on a bunch of factors, kind of like figuring out if a cheetah or a falcon is faster — both are quick, but in totally different ways.
Think of your local area network (LAN) as a highway system for data. LAN-1 and LAN-2 are simply different lanes on that highway. Just knowing the lane number doesn't tell you how fast the cars (data packets) are moving! We need more details, like the type of road (network cable), the speed limit (network hardware capabilities), and any traffic jams (network congestion).
To really understand what's happening with your LAN speeds, you need to ditch the vague "LAN-1 vs. LAN-2" idea and dig a little deeper. Are we talking about two different wired connections? Or maybe a wired versus a wireless connection? Or perhaps two completely different networks altogether? The answer to "Is LAN-1 faster than LAN-2" heavily relies on these fundamental differences.
So, before we jump to conclusions, let's put on our detective hats and start gathering some clues. We're going to investigate the underlying technology, examine the hardware involved, and sniff out any potential bottlenecks. It might sound complicated, but trust me, we'll break it down into easy-to-understand pieces. We're on a quest for ultimate LAN speed enlightenment!
![[DIAGRAM] Wireless Lan Network Diagram [DIAGRAM] Wireless Lan Network Diagram](https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-1gweJq8znso/Vpymwkrz-qI/AAAAAAAAALk/gSWlk6hiknU/s1600/23981414-LAN-Network-Diagram-Vector-Illustrator-EPS-10-for-Business-and-Technology-Concept--Stock-Vector.jpg)
The Backbone
2. Cables and Connections
Let's get down to the nitty-gritty (okay, I almost slipped up there!) of cables and connections. The type of cable you're using plays a huge role in determining your network speed. Think of it like this: a narrow, winding road won't allow cars to travel as fast as a wide, straight highway. Similarly, older or lower-quality cables can significantly limit your LAN speed.
The most common type of cable used in modern LANs is Ethernet cable, specifically Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a. These categories define the maximum speed and bandwidth the cable can support. Cat5e, while still usable, is generally the slowest and can limit speeds to 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps). Cat6 and Cat6a cables support higher bandwidth and can handle speeds up to 10 Gbps, making them ideal for faster networks.
Beyond the cable itself, the connectors and network interface cards (NICs) on your devices also matter. Ensure your devices and cables all support the same speeds. If you're using a Cat6a cable but your computer's NIC only supports 1 Gbps, you're only going to get 1 Gbps. It's like putting premium gas in a car that only needs regular — it won't hurt, but it won't help either.
So, what can you do? First, check the type of cable you're using. Look for the category printed on the cable itself. Then, verify that your network devices (computers, routers, switches) all support the desired speed. Upgrading your cables and hardware can dramatically improve your LAN speed, but make sure you're addressing the weakest link in the chain. You don't want to spend money on a fancy new cable only to find out your ancient router is the bottleneck!

Comparison Between LAN, MAN And WAN In Hindi YouTube
Wireless Wonders
3. Wireless vs. Wired
Now, let's throw Wi-Fi into the mix! Wireless connections offer convenience and flexibility, but they often come with a speed penalty compared to wired connections. Think of it like this: a wired connection is like a direct train line, while Wi-Fi is like a bus route with multiple stops and potential delays. Many factors can affect Wi-Fi speed, including distance from the router, interference from other devices, and the type of Wi-Fi technology being used.
The latest Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), offer significant improvements in speed and efficiency compared to older standards like Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n). However, to take advantage of these newer standards, both your router and your devices need to support them. If you're still using an older router, upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 model can make a noticeable difference in your wireless speeds.
Even with the latest Wi-Fi technology, wireless connections are susceptible to interference from other devices operating on the same frequency. Microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even your neighbor's Wi-Fi network can all cause interference that slows down your connection. To minimize interference, try changing the Wi-Fi channel on your router or moving your router away from potential sources of interference.
So, if you're comparing a wired LAN-1 connection to a wireless LAN-2 connection, chances are the wired connection will be faster, especially if you're using a modern Ethernet cable and network hardware. However, if both LAN-1 and LAN-2 are wireless connections, the speeds will depend on a variety of factors, including the Wi-Fi standard, distance from the router, and interference. In that case, testing the speeds of both connections at different times of day can help you determine which is generally faster.
Network Congestion and Other Culprits
4. Traffic Jams on the Information Highway
Even with the best cables and Wi-Fi technology, your LAN speed can still be affected by network congestion. Think of it like rush hour on the information highway. When too many devices are trying to use the network at the same time, speeds can slow down for everyone. This is especially common in homes with multiple users streaming video, playing online games, or downloading large files.
One way to alleviate network congestion is to prioritize traffic using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router. QoS allows you to prioritize certain types of traffic, such as video streaming or online gaming, over less time-sensitive traffic, such as file downloads. This can help ensure that critical applications get the bandwidth they need, even during peak usage times.
Another potential culprit for slow LAN speeds is outdated or misconfigured network drivers. Make sure you have the latest drivers installed for your network interface cards. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues and performance problems. Also, check your network settings to ensure they are properly configured. Incorrect IP addresses, DNS settings, or other network configurations can all lead to slow speeds.
Finally, consider the possibility of malware or other malicious software affecting your network performance. Some types of malware can consume significant bandwidth or interfere with network traffic. Run a thorough scan of your devices with a reputable antivirus program to ensure they are clean. Regularly updating your antivirus software is also crucial to protect against the latest threats. Keeping your network clean and optimized is key to maintaining consistent and reliable speeds.
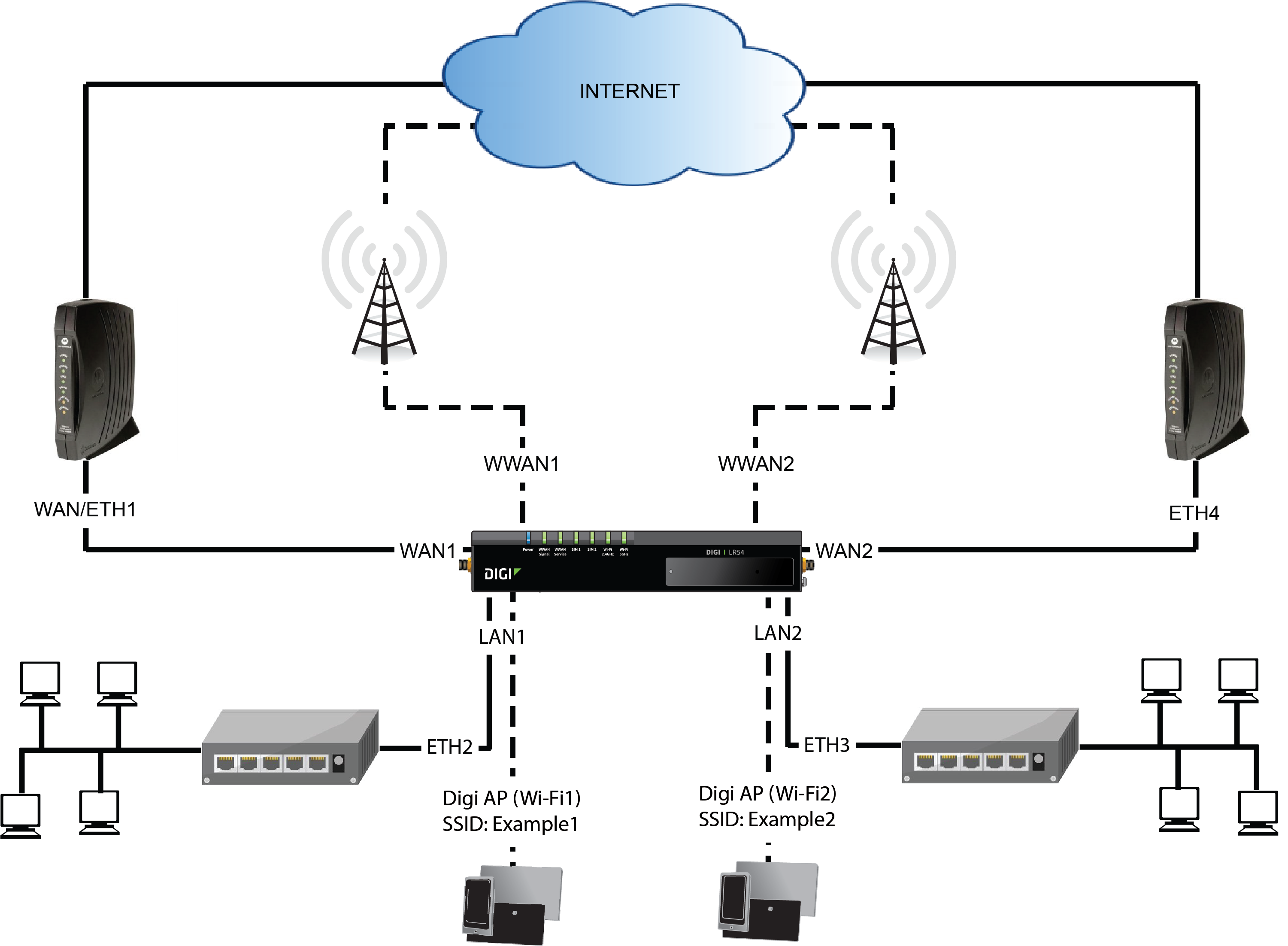
Example Configure Multiple WANs And LANs By Using The Command Line
Testing, Testing
5. Putting Speed to the Test
So, you've upgraded your cables, optimized your Wi-Fi, and cleared out any network congestion. But how do you know if it's actually made a difference? The answer is simple: test your LAN speed! There are several free and easy-to-use tools available that can help you measure your network performance and identify any remaining bottlenecks.
One popular tool is iPerf3, a command-line utility that allows you to measure the maximum achievable bandwidth between two devices on your network. It's a bit technical, but there are plenty of online tutorials that can guide you through the process. Another option is Speedtest.net, a widely used website that allows you to test your internet connection speed. While it primarily focuses on internet speeds, it can also provide a general indication of your LAN speed if you're testing between two devices on the same network.
When testing your LAN speed, it's important to perform multiple tests at different times of day to get an accurate picture of your network performance. Congestion can vary depending on the time of day, so testing during peak and off-peak hours can help you identify any potential bottlenecks. Also, make sure to close any unnecessary applications or processes that might be consuming bandwidth during the test.
By regularly testing your LAN speed, you can track your network performance over time and identify any potential problems before they become major issues. This allows you to proactively address any bottlenecks and ensure that you're getting the best possible performance from your network. Think of it like a regular checkup for your network — it helps you keep things running smoothly and prevent unexpected surprises!

FAQ
6. Your LAN Speed Questions Answered
Still scratching your head? Here are some frequently asked questions about LAN speed to help clear up any remaining confusion.
Q: Is a wired connection always faster than a wireless connection?
A: Generally, yes. Wired connections tend to offer more consistent and higher speeds compared to wireless connections due to lower latency and less interference.Q: What is the best type of Ethernet cable for fast LAN speeds?
A: Cat6a is generally considered the best option for future-proofing and supporting the highest speeds (up to 10 Gbps), but Cat6 is also a good choice for most home networks.Q: How can I improve my Wi-Fi speed?
A: Try moving your router to a central location, reducing interference from other devices, upgrading to a newer Wi-Fi standard, and using a Wi-Fi extender to improve coverage.Q: My internet speed is fast, but my LAN speed is slow. Why?
A: Your internet speed is the speed at which your data travels to and from the internet, while your LAN speed is the speed at which data travels within your local network. A slow LAN speed can be caused by outdated hardware, network congestion, or other factors that don't affect your internet connection.